
Identifying Safety Risks in Production Environments

Production environments have grown complex and their intricate operation involves numerous stakeholders. Among these stakeholders, third-party contractors play an essential role, further complicating the safety dynamics. This requires a three-tier approach – the Risk Matrix, Incident Analysis, and Workplace Inspections – each addressing specific facets of safety risks.
Risk Matrix in Production Environments
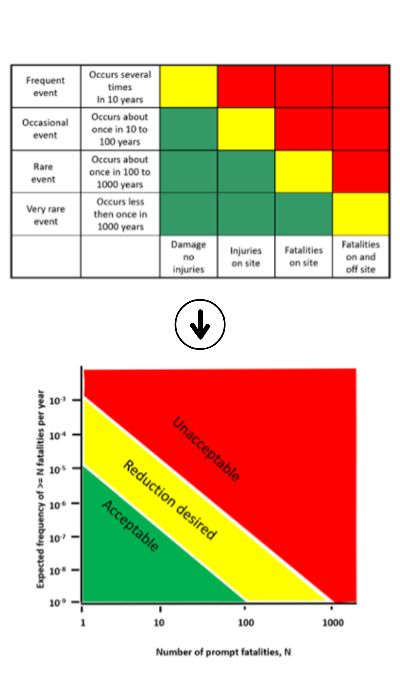
A Risk Matrix is a fundamental tool in risk management, especially in manufacturing environments. It is a graphic representation that sets the probability of risks against their potential impact. They are used in the planning phase of production projects, when assessing new processes or equipment, and regularly during the operational phase to reassess risks.
Origins
The concept of the risk matrix originated in the aviation and military industries, where it was used to evaluate the risks of missions and operations. It was later adapted for use in various industries, including manufacturing.
NASA, for example, has used the risk matrix extensively for space flight, where even small risks can have serious consequences.
Evolution in Industry
Originally risk matrices were primarily qualitative, but with advances in data analysis, they have evolved into more quantitative tools that use statistical data to more accurately assess the likelihood of risk.
Multidisciplinary Approach
This approach requires the collaboration of multiple departments, including production, safety, maintenance and sometimes even HR and finance.
Technology Integration
The integration of advanced data analysis tools and AI has improved the precision of risk assessments. These technologies can process large data sets to identify trends and patterns that human analysts may overlook.
Different Processes
When setting up new production lines or plants, a risk matrix is essential to ensure design and operation safety.
When existing production processes are changed or updated, a risk matrix helps anticipate and plan for new or changed risks.
Incident Analysis – Learning from the Past
This process involves the systematic investigation of incidents to identify causes and suggest improvements on safety protocols and procedures.
Process of Incident Analysis
It begins by gathering all relevant information about the incident. This can range from witness accounts and camera footage to detailed technical data. This information is then used for in-depth root cause analysis, often using methods such as the “5 Why’s” and “Fishbone Diagram.
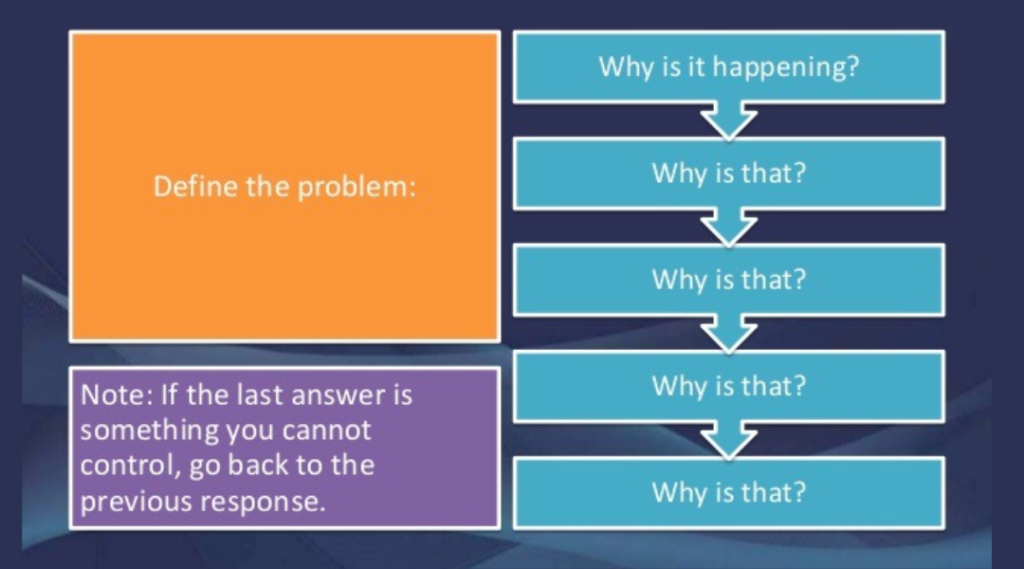
5 Why’s
This is a technique for finding the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking the question “why?” With each answer, you ask “why?” again until you reach the root cause of the problem. For example, if a machine fails, you first ask “why did the machine stop?” After the answer, you ask “why?” again. You repeat this five times (or sometimes more) until you get to the root cause.
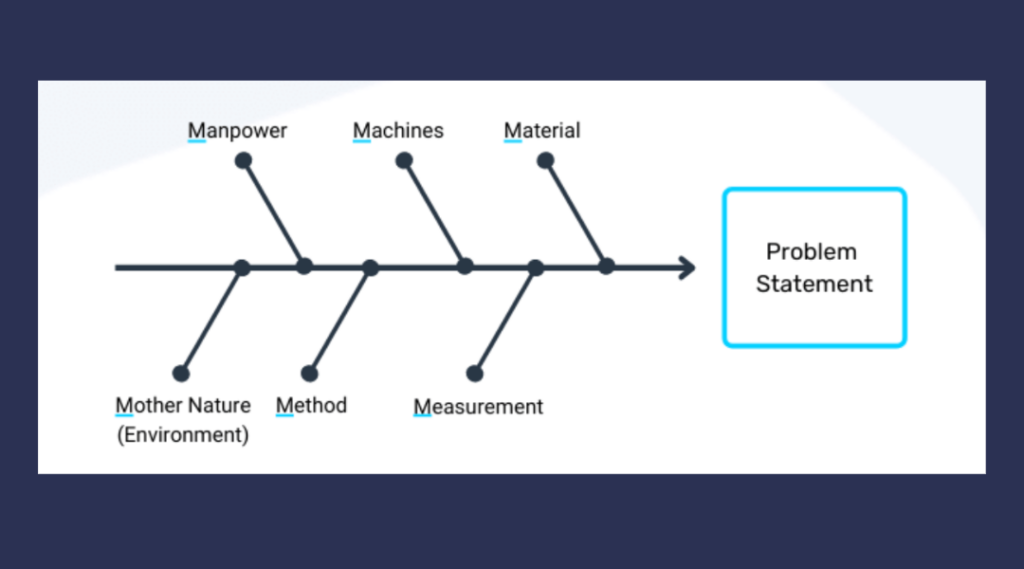
Fishbone Diagram
Also known as the Ishikawa diagram or cause-and-effect diagram. It looks like a fishbone, hence the name. You start with the problem at the head of the fish and draw lines (bones) for the different categories of possible causes, such as people, processes, technology, and materials. For each category, you brainstorm possible causes and place them along the lines. This helps visualize all possible causes of a problem and makes it easier to identify relationships between causes.
Technology and Culture
Data analysis reveals patterns in incident data, while predictive analysis helps prevent future risks. This goes hand in hand with employee engagement and regular training that fosters a culture of safety awareness and continuous improvement. Together, these elements provide a robust foundation for effective risk management and safety compliance.
Workplace Inspections – Proactive Safety Assurance
Workplace inspections have their origins in the industrial revolution. The frequency and depth of these inspections vary widely by industry depending on the risks associated with specific work environments. With the emergence of advanced technologies, such as drones and robots, inspections are becoming more efficient and safer, especially in potentially hazardous or difficult-to-access areas. The COVID-19 pandemic further tightened inspection protocols, with a new focus on hygiene and social distancing measures. Stricter regulations have led to more detailed inspection processes. In addition to ensuring physical safety, these inspections also contribute to employee morale and well-being. Moreover, they help companies save money in the long run by reducing accidents, absenteeism and insurance claims.
Efficient Safety Protocols
Regular and systematic inspections are essential for early identification and addressing hazards and risks in the workplace. These inspections include a thorough check of machinery, equipment and work processes. The use of structured checklists ensures that all relevant safety aspects are systematically assessed. Creating an effective inspection checklist requires a combination of thoroughness, clarity and user-friendliness.
Some Tips
- Determine the scope: safety, quality, maintenance, etc.
- Gather Information: existing standards, regulations and best practices.
- Clear and concise formulation.
- Organize the checklist into logical sections or categories.
- Prioritize high-risk items.
- Include symbols or images if possible.
- Leave room for specific observations.
- Test the checklist in real inspections to identify any deficiencies.
- Make sure the checklist is easily accessible, digitally if necessary.
- Keep the checklist current with regular reviews.
- Train inspectors on how to use the checklist.
- Establish a system for inspector feedback.
- Add a section for formal sign-off or verification of inspections.


With tools such as the risk matrix, incident analysis and workplace inspections, and the support of an efficient contractor management system, organizations can confidently meet the challenges of the manufacturing environment and ensure safety and compliance at all times.


















